Chapter 7 preventing perioperative disease transmission – Chapter 7: Preventing Perioperative Disease Transmission delves into the crucial measures employed to safeguard patients from infections during surgical procedures. This chapter comprehensively examines the modes of disease transmission, risk factors, and effective strategies for preventing surgical site infections.
Understanding the principles Artikeld in this chapter empowers healthcare professionals with the knowledge and tools to create a safe and infection-free environment for patients undergoing surgery.
Transmission of Perioperative Disease

During the perioperative period, patients are particularly vulnerable to disease transmission due to the invasive nature of surgical procedures and the presence of multiple healthcare providers in close proximity. The modes of disease transmission include:
- Airborne transmission:Transmission of microorganisms through droplets or aerosols generated by coughing, sneezing, or talking.
- Contact transmission:Transmission through direct or indirect contact with contaminated surfaces, equipment, or healthcare personnel.
- Bloodborne transmission:Transmission through contact with infected blood or body fluids.
Risk factors associated with increased disease transmission include:
- Prolonged surgical procedures
- Extensive tissue exposure
- Use of invasive devices
- Immunocompromised patients
- Inadequate infection control practices
Specific pathogens that can be transmitted during surgery include:
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Escherichia coli
- Hepatitis B virus
- Human immunodeficiency virus
Prevention Strategies

To prevent disease transmission in the operating room, standard precautions and infection control measures are essential. These include:
- Hand hygiene:Frequent and thorough handwashing with soap and water or alcohol-based hand rub.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE):Use of gloves, gowns, masks, and eye protection to prevent contact with contaminated materials.
- Environmental cleaning and disinfection:Regular cleaning and disinfection of surfaces, equipment, and instruments to eliminate potential sources of infection.
- Sterilization of surgical instruments:Use of heat or chemical methods to kill microorganisms on surgical instruments.
Surgical site preparation also plays a crucial role in reducing the risk of infection. This involves:
- Shaving or clipping hair at the surgical site
- Cleaning the skin with antiseptic solution
- Applying a sterile dressing to the surgical site
Antimicrobial prophylaxis is the use of antibiotics before surgery to prevent surgical site infections. Its effectiveness depends on the type of surgery, the patient’s risk factors, and the choice of antibiotic.
Surveillance and Monitoring

Surveillance and monitoring are essential for preventing perioperative disease transmission. This includes:
- Surveillance for surgical site infections (SSIs):Regular monitoring of patients after surgery for signs and symptoms of infection.
- Monitoring for other complications:Observation for any other postoperative complications that may indicate infection, such as fever, pain, or wound drainage.
- Feedback and quality improvement initiatives:Analysis of surveillance data to identify areas for improvement in infection control practices.
Feedback and quality improvement initiatives are crucial for reducing the incidence of perioperative disease transmission. By identifying and addressing areas for improvement, healthcare facilities can continuously enhance their infection control practices and patient outcomes.
Education and Training
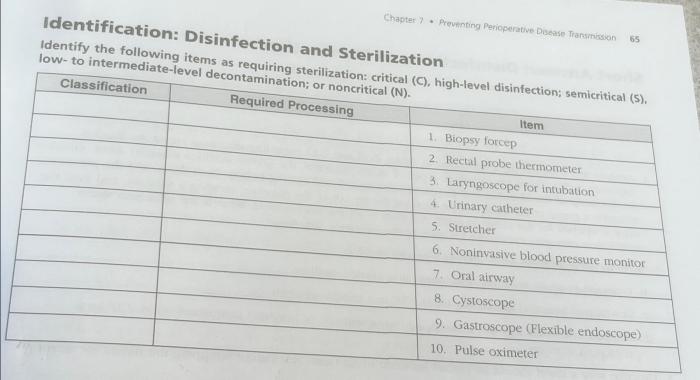
Education and training for healthcare professionals are essential for preventing perioperative disease transmission. Effective programs should include:
- Basic infection control principles:Understanding the modes of disease transmission and the importance of standard precautions.
- Specific surgical site infection prevention practices:Surgical site preparation, antimicrobial prophylaxis, and surveillance for SSIs.
- Hands-on training:Practical demonstrations and simulations to improve infection control skills.
Simulation and hands-on training are particularly valuable in improving infection control practices. By providing a realistic environment for practicing infection control techniques, healthcare professionals can enhance their skills and confidence in preventing perioperative disease transmission.
FAQ: Chapter 7 Preventing Perioperative Disease Transmission
What are the primary modes of disease transmission during surgery?
Contact with contaminated surfaces, instruments, or bodily fluids.
What is the role of antimicrobial prophylaxis in preventing surgical site infections?
Antimicrobial prophylaxis involves administering antibiotics before surgery to reduce the risk of infection.
How does surveillance and monitoring contribute to preventing perioperative disease transmission?
Surveillance and monitoring allow for early detection and prompt intervention in case of potential infections.