Acids bases ph and buffers pre lab – Delving into the realm of acids, bases, pH, and buffers, this pre-lab exploration unveils the fundamental principles that govern these chemical entities. Understanding their behavior and interactions is crucial for a wide range of scientific disciplines, including chemistry, biology, and medicine.
In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of acids and bases, explore the significance of pH in biological systems, and delve into the mechanisms by which buffers maintain a stable pH. By equipping ourselves with this knowledge, we lay the foundation for successful experimentation and a deeper understanding of the chemical world.
Acids and Bases

Acids and bases are two of the most fundamental concepts in chemistry. They play a vital role in many chemical reactions and are essential for life as we know it.
The Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases defines an acid as a substance that can donate a proton (H+), and a base as a substance that can accept a proton.
Strong and Weak Acids and Bases
Acids and bases can be classified as either strong or weak. Strong acids and bases completely dissociate in water, while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate.
Some examples of strong acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulfuric acid (H2SO4), and nitric acid (HNO3). Some examples of strong bases include sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), and calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2).
Properties of Acids and Bases
Acids and bases have a number of characteristic properties, including their pH and conductivity.
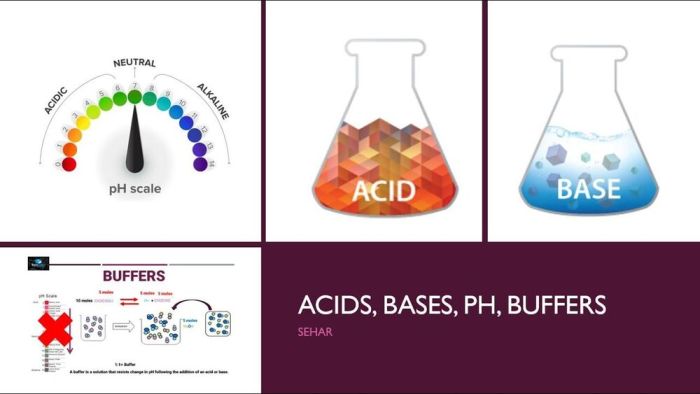
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity or basicity. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most basic. A neutral solution has a pH of 7.
Acids have a pH below 7, while bases have a pH above 7.
Conductivity is a measure of a solution’s ability to conduct electricity. Acids and bases are good conductors of electricity, while pure water is a poor conductor.
pH and Buffers: Acids Bases Ph And Buffers Pre Lab
Concept of pH
pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution. It is defined as the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration.
The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most basic. A neutral solution has a pH of 7.
Importance of pH in Biological Systems
pH is critical for life as we know it. The pH of the human body is tightly regulated within a narrow range of 7.35 to 7.45.
Changes in pH can have a profound effect on the function of enzymes and other proteins. For example, a drop in pH can cause enzymes to denature, which can lead to cell death.
Buffers
Buffers are solutions that resist changes in pH. They are composed of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
When a small amount of acid or base is added to a buffer, the buffer will react to neutralize the added acid or base, thereby preventing a significant change in pH.
Buffers are essential for maintaining a stable pH in biological systems. For example, the bicarbonate buffer system helps to maintain the pH of the blood.
Pre-Lab Preparation

Safety Precautions
When working with acids and bases, it is important to take the following safety precautions:
- Wear gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat.
- Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Never mix acids and bases directly.
- Always add acid to water, not vice versa.
- Dispose of acids and bases properly.
Materials and Equipment
The following materials and equipment will be used in the pre-lab:
- 10 mL of 0.1 M HCl
- 10 mL of 0.1 M NaOH
- 100 mL of distilled water
- pH meter
- Conductivity meter
Procedures
The following procedures will be followed during the pre-lab:
- Measure the pH of the 0.1 M HCl solution.
- Measure the pH of the 0.1 M NaOH solution.
- Measure the conductivity of the 0.1 M HCl solution.
- Measure the conductivity of the 0.1 M NaOH solution.
- Mix 5 mL of the 0.1 M HCl solution with 5 mL of the 0.1 M NaOH solution.
- Measure the pH of the mixed solution.
- Measure the conductivity of the mixed solution.
Key Concepts and Equations, Acids bases ph and buffers pre lab
The following key concepts and equations will be covered in the pre-lab:
- The Brønsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases
- The pH scale
- The importance of pH in biological systems
- The role of buffers in maintaining a stable pH
- The equations for the dissociation of acids and bases
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid?
Strong acids completely dissociate in water, releasing all their hydrogen ions, while weak acids only partially dissociate, resulting in a lower concentration of hydrogen ions.
How does a buffer work?
A buffer resists changes in pH by absorbing or releasing hydrogen ions, maintaining a relatively stable pH within a specific range.
Why is pH important in biological systems?
pH plays a crucial role in enzyme activity, protein structure, and cell function. Deviations from optimal pH levels can disrupt these processes and impair cell viability.