Introducing a glycerol molecule and three butyric, a captivating tale of chemical interaction that unveils a fascinating world of molecular transformations and practical applications. This journey begins with an exploration of the structures and properties of glycerol and butyric acid, setting the stage for an in-depth examination of their intriguing reaction.
Delving deeper, we elucidate the step-by-step mechanism of this reaction, unraveling the intricacies of bond formation and cleavage that lead to the creation of novel products. These products hold immense significance in various industries, and we delve into their diverse applications, highlighting their benefits and limitations.
Introduction: A Glycerol Molecule And Three Butyric
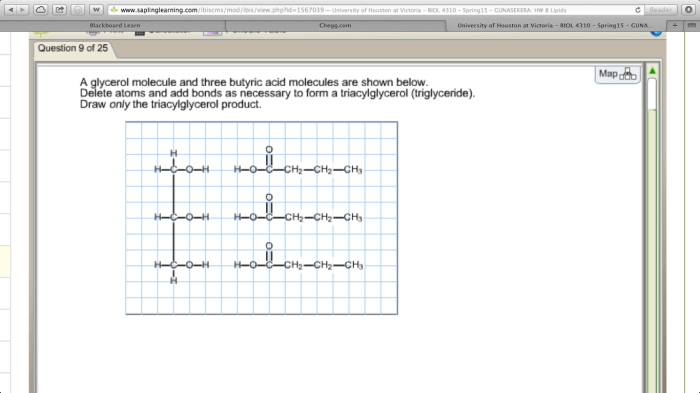
Glycerol and butyric acid are two important organic compounds with distinct chemical structures and properties. Glycerol is a trihydroxy alcohol, while butyric acid is a four-carbon carboxylic acid.
Glycerol is a viscous, colorless liquid with a sweet taste. It is soluble in water and has a density of 1.26 g/cm 3. Butyric acid is a colorless liquid with a strong, unpleasant odor. It is insoluble in water and has a density of 0.95 g/cm 3.
Chemical Structure
The chemical structure of glycerol is CH 2OHCHOHCH 2OH. It consists of a central carbon atom bonded to three hydroxyl groups (-OH). The chemical structure of butyric acid is CH 3CH 2CH 2COOH. It consists of a four-carbon chain with a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) at one end.
Properties
Glycerol is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications. It is used as a humectant, solvent, and plasticizer. Butyric acid is used as a flavoring agent and preservative. It is also used in the production of pharmaceuticals and cosmetics.
Reaction between Glycerol and Butyric Acid
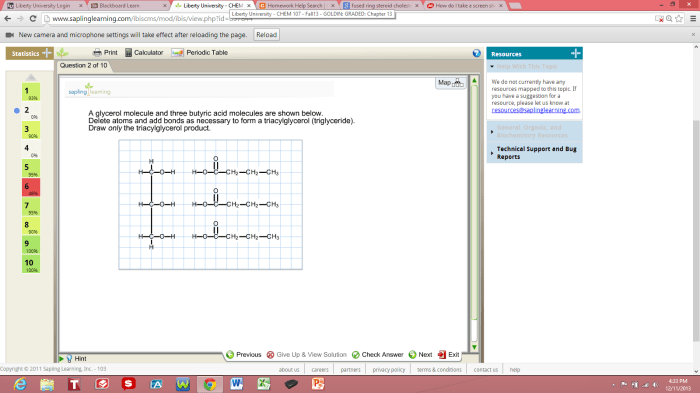
Glycerol and butyric acid undergo a reaction known as esterification, which involves the formation of an ester bond between the hydroxyl group of glycerol and the carboxyl group of butyric acid.
Mechanism of the Reaction
The reaction proceeds through a two-step mechanism:
- Proton transfer:Butyric acid donates a proton to glycerol, forming a protonated glycerol molecule.
- Nucleophilic attack:The protonated glycerol molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon of butyric acid, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
- Elimination of water:The tetrahedral intermediate undergoes elimination of water, resulting in the formation of the ester product.
Products of the Reaction
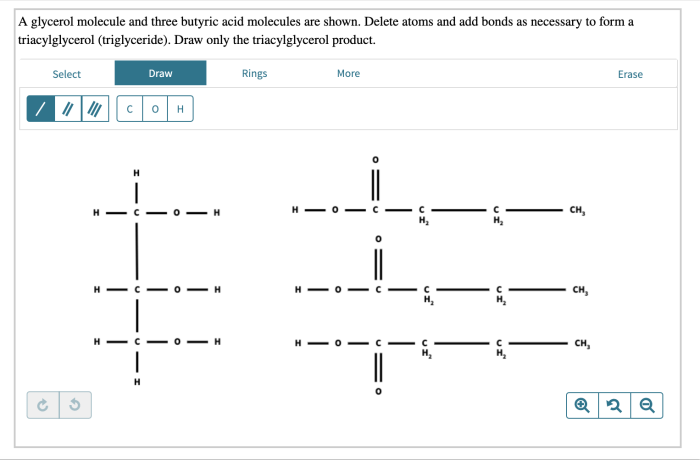
The reaction between glycerol and butyric acid produces the ester product known as tributyrin, which is a triglyceride with three butyric acid molecules attached to the glycerol backbone.
Applications of the Reaction Product
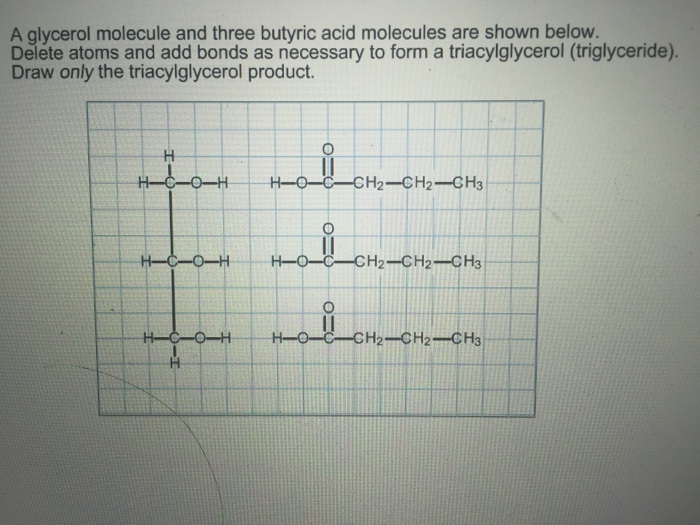
The reaction product of glycerol and butyric acid, known as glyceryl tributyrate, has various applications in different industries.
One significant application is in the food industry, where glyceryl tributyrate is used as a food additive. It is commonly employed as an emulsifier, helping to blend immiscible ingredients like oil and water, thereby preventing separation and enhancing the overall texture of food products.
Additionally, glyceryl tributyrate contributes to the flavor and aroma of certain food items, particularly in baked goods and confectioneries.
Pharmaceutical Industry
In the pharmaceutical industry, glyceryl tributyrate finds use as an excipient, a substance added to medications to improve their stability, absorption, or delivery. It is particularly beneficial in formulations intended for oral administration, where it acts as a solubilizing agent, enhancing the bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.
Moreover, glyceryl tributyrate possesses antimicrobial properties, making it a valuable ingredient in topical preparations for treating skin infections.
Personal Care and Cosmetics
Glyceryl tributyrate has gained prominence in the personal care and cosmetics industry due to its emollient properties. It is incorporated into skincare products, such as lotions, creams, and soaps, where it helps soften and smooth the skin, reducing dryness and improving its overall appearance.
Furthermore, glyceryl tributyrate exhibits anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, making it a suitable ingredient for products aimed at sensitive or aging skin.
Benefits and Limitations
The use of glyceryl tributyrate offers several benefits. It is generally considered safe for consumption and application, with a low risk of adverse effects. Its emulsifying properties enhance the texture and stability of food products, while its antimicrobial activity contributes to their preservation.
In pharmaceutical formulations, glyceryl tributyrate improves drug solubility and bioavailability, enhancing the effectiveness of medications. In personal care products, it promotes skin hydration and health, making it a valuable ingredient for various skincare applications.
However, certain limitations associated with glyceryl tributyrate should be noted. It can be susceptible to hydrolysis, particularly under acidic conditions, which may affect its stability and functionality. Additionally, the production of glyceryl tributyrate involves the use of chemical catalysts, which must be carefully controlled to ensure product purity and minimize the formation of unwanted byproducts.
Safety Considerations
Glycerol and butyric acid are chemicals that require proper handling and disposal to ensure safety. Understanding the hazards associated with these compounds is crucial for preventing accidents and minimizing risks.
Glycerol is a non-toxic and non-flammable liquid, but it can cause skin irritation and eye damage. Butyric acid, on the other hand, is a corrosive and flammable liquid that can cause severe burns, eye damage, and respiratory irritation.
Safety Guidelines for Handling
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat, when handling glycerol and butyric acid.
- Handle butyric acid in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhalation of vapors.
- Avoid contact with skin and eyes. If contact occurs, flush the affected area with plenty of water and seek medical attention immediately.
- Keep these chemicals away from heat, sparks, and open flames to prevent fire hazards.
Proper Disposal Methods, A glycerol molecule and three butyric
- Glycerol can be disposed of by pouring it down the drain with plenty of water.
- Butyric acid must be neutralized before disposal. To neutralize butyric acid, slowly add a base, such as sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate, to the acid until the pH is between 6 and 8. The neutralized solution can then be disposed of by pouring it down the drain with plenty of water.
FAQ Overview
What is the significance of the reaction between glycerol and butyric acid?
This reaction is crucial for the production of triglycerides, which are essential components of fats and oils.
How does the structure of glycerol and butyric acid influence their reactivity?
Glycerol’s three hydroxyl groups and butyric acid’s carboxylic acid group provide functional groups that facilitate the esterification reaction.
What are the safety considerations when working with glycerol and butyric acid?
Both compounds can cause skin irritation and respiratory problems, necessitating proper handling and disposal.