Adp 6 22 army leadership – ADP 6-22 Army Leadership is the definitive guide for military leaders, providing a comprehensive framework for understanding and applying effective leadership principles. This document Artikels the core concepts, responsibilities, and competencies that are essential for leaders to succeed in today’s complex and demanding operational environment.
ADP 6-22 emphasizes the importance of mission accomplishment, ethical decision-making, and team dynamics. It provides practical guidance on developing leadership competencies, fostering leader development, and communicating effectively in diverse situations. By embracing the principles Artikeld in ADP 6-22, leaders can inspire their teams, achieve mission success, and make a lasting impact on the organization.
ADP 6-22 Army Leadership
ADP 6-22 Army Leadership is the foundational document that defines the Army’s philosophy and approach to leadership. It provides a comprehensive framework for developing and training leaders who are capable of leading effectively in complex and challenging environments.
ADP 6-22 emphasizes the importance of character, competence, and commitment as the cornerstones of effective leadership. It Artikels the key principles and concepts that guide leaders in their decision-making, problem-solving, and communication.
Key Principles of ADP 6-22
The key principles of ADP 6-22 include:
- Mission Command:Leaders empower subordinates to make decisions and take action within the commander’s intent.
- Decentralized Execution:Leaders delegate authority and responsibility to lower levels to foster initiative and adaptability.
- Unified Action:Leaders coordinate and synchronize efforts across all elements of the organization to achieve common goals.
- Leadership Development:Leaders continuously develop themselves and their subordinates to enhance their leadership capabilities.
- Ethical Decision-Making:Leaders make decisions based on sound ethical principles and values.
Impact on Leadership Development and Training
ADP 6-22 has had a significant impact on leadership development and training within the Army. It has:
- Established a common language and framework for leadership across the Army.
- Provided a roadmap for developing leaders at all levels.
- Enhanced the focus on ethical decision-making and character development.
- Promoted a culture of continuous learning and self-improvement.
Mission
Mission, the driving force behind any military operation, is a concise statement of the task, purpose, and desired outcome. In ADP 6-22 Army Leadership, mission takes center stage, guiding leaders in setting clear objectives and directing their actions.
Leaders bear the responsibility of understanding, interpreting, and executing missions effectively. They must possess the authority to make decisions, allocate resources, and command their subordinates to achieve mission success.
Examples of Mission Application
Mission plays a crucial role in various operational scenarios:
- Combat Operations:Mission defines the specific objectives to be achieved during combat, such as capturing a strategic location or neutralizing enemy forces.
- Humanitarian Assistance:Mission Artikels the goals of providing aid, relief, and support to disaster-stricken areas or conflict zones.
- Peacekeeping Operations:Mission establishes the mandate for maintaining peace and stability in post-conflict environments, often involving monitoring ceasefires or facilitating negotiations.
- Training Exercises:Mission provides the framework for realistic and challenging training scenarios, testing the readiness and capabilities of units.
Leadership Competencies
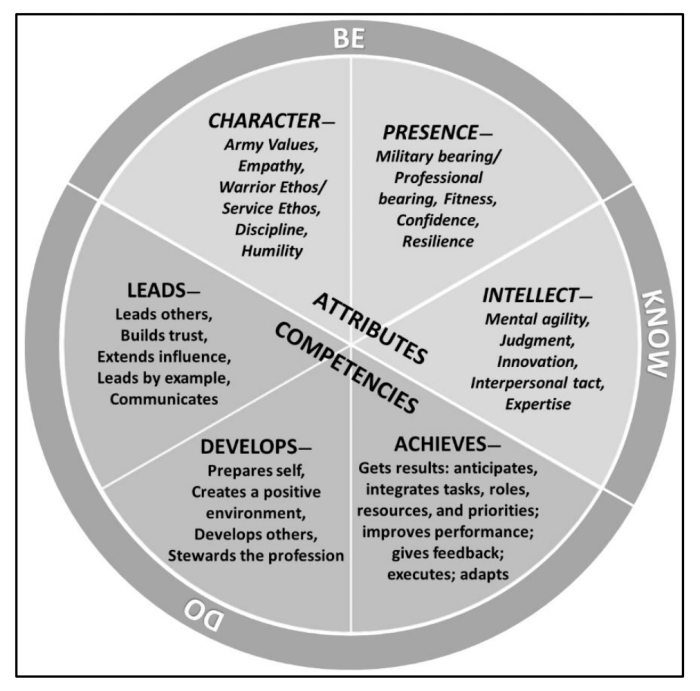
Leadership competencies are a set of skills, knowledge, and abilities that are essential for effective leadership in the Army. These competencies are defined in ADP 6-22 and are organized into four domains: Leading, Developing, Achieving, and Learning.
Each competency is important for different aspects of leadership. For example, the Leading domain includes competencies such as Leading with Purpose and Communicating Effectively, which are essential for inspiring and motivating followers. The Developing domain includes competencies such as Developing Others and Coaching, which are essential for helping followers grow and develop.
The Achieving domain includes competencies such as Setting Direction and Executing Plans, which are essential for achieving mission objectives. The Learning domain includes competencies such as Seeking Feedback and Adapting to Change, which are essential for continuous improvement.
ADP 6-22 Army Leadership provides a comprehensive framework for effective leadership in the military. To enhance your understanding of leadership concepts, consider exploring AP Gov Chapter 11 Vocab . This resource offers a detailed glossary of terms relevant to leadership and governance, further enriching your knowledge in this domain.
Developing Leadership Competencies
There are a number of ways to develop and enhance leadership competencies. One way is through formal training and education. The Army offers a variety of leadership courses and programs that can help leaders develop the skills and knowledge they need to be successful.
Another way to develop leadership competencies is through on-the-job experience. By taking on challenging assignments and working with different people, leaders can learn and grow in their roles. Finally, leaders can also develop their competencies through self-study and reflection. By reading books and articles about leadership, and by taking time to reflect on their own experiences, leaders can gain insights and improve their skills.
Leader Development
The Army’s approach to leader development is Artikeld in ADP 6-22 and emphasizes the importance of continuous learning and growth for leaders at all levels. The Army recognizes that effective leaders are not born but made through a combination of training, experience, and mentorship.To
foster leadership growth, the Army has implemented various programs and initiatives. These include formal training programs such as the Basic Officer Leadership Course (BOLC), the Captain’s Career Course (CCC), and the Command and General Staff College (CGSC). In addition, there are numerous on-the-job training opportunities, such as assignments to leadership positions and participation in exercises and deployments.
Ethical Decision-Making

Ethical decision-making is crucial for Army leaders to maintain integrity, trust, and the well-being of their subordinates and the organization. ADP 6-22 emphasizes ethical principles and values that guide leaders in making sound decisions, even in challenging situations.
Leaders must uphold the Army Values of loyalty, duty, respect, selfless service, honor, integrity, and personal courage. These values serve as a moral compass, guiding leaders in their actions and decisions. Additionally, leaders must adhere to the ethical principles of justice, equality, fairness, and compassion.
Ethical Decision-Making Process
When faced with ethical dilemmas, leaders should engage in a structured decision-making process:
- Identify the ethical issue:Clearly define the ethical dimensions of the situation.
- Gather information:Seek relevant facts and perspectives to gain a comprehensive understanding of the issue.
- Analyze the issue:Consider the potential consequences of different courses of action, weighing the ethical implications of each.
- Make a decision:Choose the course of action that aligns with ethical principles and values.
- Take action:Implement the decision and be prepared to justify it to others.
- Reflect and evaluate:Assess the outcomes of the decision and learn from the experience to improve future ethical decision-making.
Consequences of Unethical Behavior, Adp 6 22 army leadership
Unethical behavior can have severe consequences for leaders and the organization, including:
- Loss of trust and credibility
- Damage to reputation
- Legal and disciplinary action
- Erosion of morale and unit cohesion
- Compromise of mission accomplishment
Importance of Accountability
Leaders are accountable for their ethical decisions and actions. They must be transparent and open to scrutiny. By holding themselves accountable, leaders set a positive example and foster a culture of integrity within the organization.
Team Dynamics
In ADP 6-22, team dynamics play a pivotal role in mission accomplishment and organizational effectiveness. Teams are the backbone of any military unit, and their success hinges on the synergy and collaboration among their members.
Within a team, different roles and responsibilities are assigned to each individual, ensuring a well-rounded and cohesive unit. Leaders provide guidance, motivation, and direction, while followers contribute their expertise, skills, and perspectives. The effective execution of these roles is essential for team success.
Strategies for Building and Maintaining Effective Teams
Building and maintaining effective teams is a multifaceted endeavor that requires conscious effort and commitment from all members. ADP 6-22 Artikels several strategies to foster team cohesion and productivity:
- Establish clear goals and objectives:Teams must have a shared understanding of their purpose and the desired outcomes. Clear goals provide direction and motivation, aligning everyone’s efforts towards a common target.
- Foster open communication:Teams thrive when members feel comfortable expressing their ideas, concerns, and feedback. Encouraging open dialogue promotes trust, understanding, and problem-solving.
- Build trust and respect:Trust is the foundation of any successful team. Leaders must create an environment where members feel valued, respected, and supported. This fosters a sense of camaraderie and encourages individuals to take risks and contribute to the team’s success.
- Promote diversity and inclusion:Teams with diverse perspectives and backgrounds are more innovative and adaptable. Leaders should actively promote inclusion, ensuring that all members feel welcome and have an equal opportunity to contribute.
- Provide ongoing training and development:Continuous learning is essential for team growth and effectiveness. Leaders should provide opportunities for members to enhance their skills, knowledge, and competencies.
Communication: Adp 6 22 Army Leadership
Effective communication is essential for successful leadership. ADP 6-22 Artikels several principles for effective communication, including clarity, conciseness, and active listening.There are different types of communication, each with its appropriate use in leadership situations. Verbal communication, including face-to-face conversations, phone calls, and video conferences, allows for immediate feedback and clarification.
Nonverbal communication, such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice, can convey subtle messages and emotions. Written communication, including emails, letters, and reports, provides a permanent record and allows for careful consideration.To improve communication skills and build trust, leaders can practice active listening, seek feedback, and use clear and concise language.
Active listening involves paying attention to both verbal and nonverbal cues, asking clarifying questions, and summarizing key points. Feedback provides leaders with valuable insights into their communication style and helps them make necessary adjustments. Clear and concise language ensures that messages are easily understood and interpreted correctly.
Situational Leadership
Situational leadership is a theory that proposes that the most effective leadership style depends on the situation. There are four main leadership styles: directive, coaching, supportive, and delegating. Each style is most appropriate in different situations, depending on the maturity and competence of the followers.
ADP 6-22 emphasizes the importance of situational leadership and provides guidance on how to use it to achieve mission success. The manual states that “leaders must be able to adapt their leadership style to the situation and the needs of their followers.”
It also provides a table that summarizes the four leadership styles and their appropriate uses.
Directive Leadership
Directive leadership is most appropriate when followers are inexperienced or lack competence. This style involves giving clear instructions and closely supervising followers. Directive leaders tell their followers what to do, how to do it, and when to do it. They provide little opportunity for input from followers.
Coaching Leadership
Coaching leadership is most appropriate when followers have some experience but still need guidance and support. This style involves providing followers with feedback and support while allowing them to make some decisions on their own. Coaching leaders help their followers to develop their skills and knowledge.
Supportive Leadership
Supportive leadership is most appropriate when followers are experienced and competent. This style involves providing followers with emotional support and encouragement. Supportive leaders listen to their followers’ concerns and help them to solve problems. They create a positive and supportive work environment.
Delegating Leadership
Delegating leadership is most appropriate when followers are highly experienced and competent. This style involves giving followers the authority to make decisions and take action. Delegating leaders trust their followers to complete tasks without close supervision. They provide followers with the resources and support they need to be successful.
Situational leadership is a valuable tool that can help leaders to achieve mission success. By adapting their leadership style to the situation and the needs of their followers, leaders can create a positive and productive work environment that fosters follower development and mission accomplishment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of ADP 6-22 Army Leadership?
ADP 6-22 Army Leadership provides a comprehensive framework for understanding and applying effective leadership principles within the Army.
What are the key principles Artikeld in ADP 6-22?
ADP 6-22 emphasizes mission accomplishment, ethical decision-making, team dynamics, leadership competencies, and leader development.
How does ADP 6-22 contribute to leadership development?
ADP 6-22 provides practical guidance on developing leadership competencies, fostering leader development, and communicating effectively in diverse situations.